Survey Research
Survey for Research
The survey research is a systematic approach that involves gathering information from individuals through their responses to questions and aims to draw conclusions.

Survey: Introduction
Researchers analyze the data they collect from surveys to identify trends, draw conclusions, and make informed decisions. They use survey results to gain insights into the needs and expectations of a particular group, which can guide the development of products or services, inform policy decisions, or evaluate the effectiveness of existing initiatives.
According to Dr. Dillman survey is "A systematic method for gathering information from a sample of individuals or organizations, with the goal of describing and understanding some phenomenon of interest."
The definition given by Dr. Dillman validates the real importance as he emphasizes the importance of designing surveys with a clear understanding of the research question or objective, and carefully selecting a representative sample of the target population in his definition.

Characteristics Of Survey
- Sampling
When conducting a survey, people who will be answering the questionnaire are known as the sample. To ensure that the insights generated are accurate, the sample should include people who possess the demographic characteristics, relevant to the study and who can answer the questions in a meaningful way. The quality of the results improves as the sample becomes more representative. - Survey Questions: How to create effective questions?
The questions in a survey are the key to generating meaningful insights. Here are some important things to keep in mind:- The accuracy of the data collected and response rates depend largely on the nature of the survey questions, regardless of the method of administration.
- When creating multiple-choice questions, it's important to determine the type of rating scale to be used (nominal, ordinal, ratio, or interval) before developing the questionnaire.
- Survey Logic: How to ensure logical flow in your survey?
The logic behind a survey is crucial to its success. Researchers use logic to ask questions that are relevant to the respondents based on their previous answers. Skip logic (a feature that changes what question or page a respondent sees next based on how they answer the current question) in surveys allows researchers to create intelligent surveys that expose respondents to new questions based on their answers to screening questions. Some key characteristics of survey skip logic and branching include:- Designing the logic behind the questions to avoid presenting irrelevant questions to respondents.
- Survey logic can be implemented through conditional or unconditional branching, as well as utilizing parameters such as piping data, question randomization, and link quota, depending on the study's objectives.
- Survey Methods
Researchers use survey methods to gather detailed responses from a specific sample population that they have predetermined within the larger target population. Survey methods involve using instruments and processes that ask various types of questions to collect data. Strategies used to boost survey response rates include providing incentives, communicating clearly, and sending follow-up reminders. The objective of survey research is to obtain accurate and reliable data that researchers can analyze to gain insights and draw conclusions about the target population.

Understanding and Evaluating Survey Research
This scientific investigation or systematic approach involves gathering information from individuals through their responses to questions and aims to draw conclusions about a larger population. Survey research includes various methods of recruitment, data collection, and instrumentation, and frequently involves statistical analysis. Often used in social and psychological research to understand human behavior, survey research is a scientific approach that employs surveys to investigate a research question or hypothesis, while a survey is simply a tool for gathering information.
Survey research has become more scientific in recent times, with tested strategies on who to include, how to distribute, and when to follow up with non-responders to ensure high-quality outcomes.
However, there is the potential for bias in survey research, which can affect the accuracy of the results. To draw appropriate conclusions from survey research, it is important to understand the types and sources of error that can occur and the techniques for reducing them.

What is Survey Software?
You can leverage this innovative solution in many avenues, including customer feedback, employee satisfaction, post-event analysis, market research, and academic program assessment. Survey software empowers you to ask relevant questions, engage your audience, analyze feedback, and take informed action based on insights gleaned from the results. In essence, survey software streamlines the entire survey process and delivers actionable feedback that can drive impactful change.
Benefits of Surveys in Research
Efficient data collection
Standardized data collection
Anonymity
Cost-effective
Provides quantitative data
Provides insights into attitudes and beliefs
Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
On the other hand, quantitative research is a data-driven, systematic technique that employs statistical, logical, and mathematical tools to quantify and measure observable phenomena. It's all about turning numbers into insights.
According to C. Wright Mills, "Quantitative researchers aim to produce statistical laws of human behavior, while qualitative researchers seek to uncover deep meaning and understanding of a phenomenon as experienced by participants in natural settings."
However, we believe there are some other distinct differences between qualitative and quantitative research that you must know.
- Approach: Qualitative research is subjective, as researchers are involved, while quantitative research is objective, with researchers striving to achieve precise analysis to answer inquiries.
- Purpose: Qualitative research is exploratory, while quantitative research is definitive.
- Sampling: Qualitative research uses purposive sampling, while quantitative research uses random sampling.
- Data Collection: Qualitative research collects verbal data, while quantitative research collects measurable data.
- Analysis Elements: Qualitative research uses words, pictures, and objects, while quantitative research uses numerical data.
- Purpose: Qualitative research aims to discover ongoing ideas, while quantitative research seeks to examine cause and effect.
- Methods: Qualitative research uses in-depth interviews and focus groups, while quantitative research uses structured interviews and observations.
- Result: Qualitative research establishes initial understanding, while quantitative research provides a final course of action.

Is Survey Research Qualitative or Quantitative?
Surveys can also be designed with closed-ended questions that provide quantitative data, which can be analyzed statistically to draw conclusions about the research topic. Using a mixed-methods approach enables researchers to gather both qualitative and quantitative data, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
Thus, survey research is a valuable tool that can be adapted to suit specific research needs and can offer a range of insights through its diverse data collection methods.
Let's take an example to understand how you can use both qualitative and quantitative approaches for survey research.
Research problem: How effective are different teaching methods in improving students' learning outcomes in a particular subject?
- Quantitative approach: You can use close-ended survey questions to rate teaching methods on a scale of 1-5, and analyze the data statistically to determine which method is most effective.
- Qualitative approach: You can even conduct in-depth interviews with open-ended questions to explore students' experiences and gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives on different teaching methods.

What are Qualitative Survey Questions?
Quantitative research is used to answer questions that deal with measurable variables, such as numerical data or statistical analysis. Here are a few examples to make this point more digestible for you.
- How many hours per week do people spend on social media?
- What percentage of students prefer online learning over traditional in-person classes?
- How much money do customers typically spend on a particular product or service?
- What is the average age of people who buy a certain brand of car?
- How many people in a given population have been vaccinated against a certain disease?

What are Quantitative Survey Questions?
- What are the experiences of parents raising a child with autism?
- How do patients perceive the quality of healthcare services in rural areas?
- What are the barriers to accessing mental health services among marginalized communities?
- How do teachers perceive the impact of technology on students' learning outcomes?
- What are the cultural values that shape the dietary habits of a particular community?
- How do employees experience workplace diversity and inclusion initiatives?
Hybrid Research: How to Combine Qualitative & Quantitative Methods
Ensure Proper Planning
Never Forget the 'Golden Rule'
Keep The Hybrid Market Research Consistent
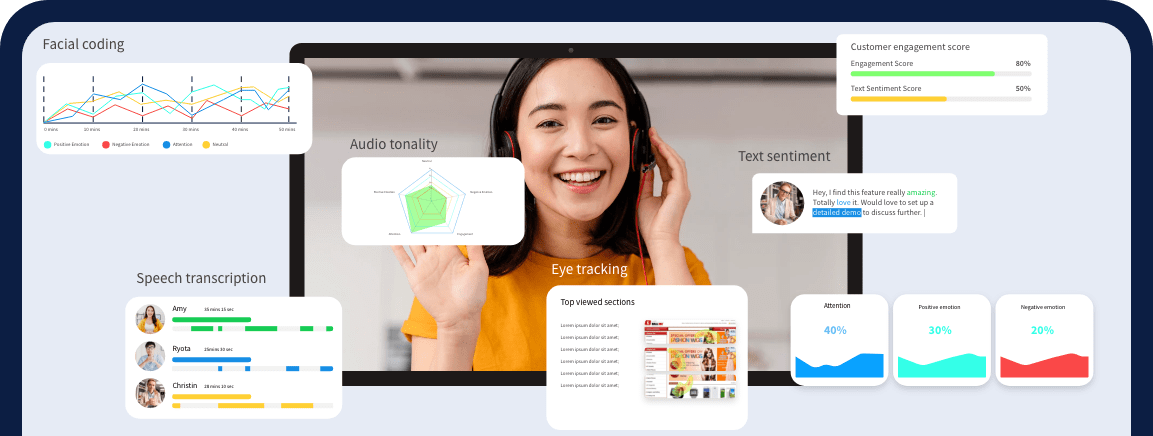
Request a Live Demo!
See how Facial Coding can
help your business
Book your slot now!
Other technologies similar to facial coding
Latest from our Resources
Using Emotion AI to Spot and Smooth Out Digital Experience Pain Points
Using Emotion AI to Spot and Smooth Out Digital Experience Pain Points Imagine you own a high-end retail store. A customer walks in, looks at a product, scowls in confusion, sighs loudly, and walks out. You saw it happen. You know exactly why you lost the
Read MoreWhy E-Commerce Needs Data-Driven Customer Journey Maps
Why E-Commerce Needs Data-Driven Customer Journey Maps Walk into any E-commerce Director’s office, and you will likely see it: The
Read nowHow Facial Coding Helps Brands Test Audience Reactions to TV Promos and Long-Format Ads
How Facial Coding Helps Brands Test Audience Reactions to TV Promos and Long-Format Ads In the world of advertising, the stakes have never
Read now