AI for Market Research
AI for Market Research
If you’re a market research professional, business owner, or a marketer, you will most certainly resonate with the core proposition here. With the increasing complexity of datasets and constantly evolving customer behaviour spectrum, moving beyond traditional market research methodologies is paramount. One avenue that facilitates this with great efficiency is AI. Using AI for market research offers certain advantages, the most important one being the immense processing capabilities of modern computers coupled with the versatility of machine learning models that can do anything from uncovering hidden patterns to surfacing emotional insights.

Unveiling the Impact of AI in Market Research
pend money. However, they aren’t so good at qualitative analysis where the parameters are subjective and can’t be measured numerically. For instance, using traditional market research to answer questions like “What exactly does a customer feel when he/she interacts with the product?” may prove to be ineffective.
Let’s understand why.
Suppose a researcher conducts a one-on-one interview with several participants to find out how they feel when they interact with a certain product. The interviewer asks several questions and the respondent answers them. Now, is there any way the researcher can tell whether the respondent was telling the truth?
No, there’s not.
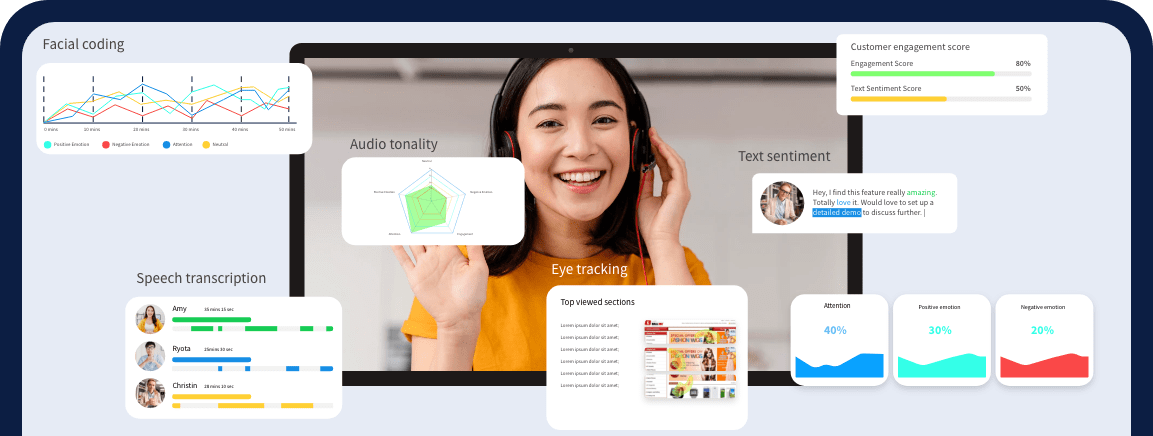
This is where most traditional market research avenues start to fail. There are visual and tonal cues linked to consumer behaviour that are often ignored by traditional market research methodologies. With AI-based tools like emotion AI that can use ML models and advanced Facial Action Coding System along with retina tracking and tonal analysis to uncover emotional heatmaps of research participants. Emotional insights can be coupled with traditional insights to differentiate between honest and dishonest responses, and then make decisions.

AI in Quantitative Analysis
Moreover, AI plays a pivotal role in deciphering text structures, recognizing sentiments, and extracting key themes from unstructured datasets like customer reviews and social media posts. AI models can process and analyse textual and multimedia content to uncover hidden insights about customer opinions, biases, and natural inclinations. AI-driven voice recognition systems facilitate the transcription and analysis of recorded interviews and focus groups, helping researchers uncover conversational patterns and extract meaningful insights at scale.
By automating coding and categorization processes, AI accelerates qualitative analysis workflows, enhancing the depth and accuracy of qualitative research outcomes. Lightbulb’s premier quantitative analysis tool called Insights Pro Quantitative offers a unique feature set that facilitates tasks like creative testing, user journey testing, and UI/UX testing while automating repetitive tasks making the overall process smarter and more efficient. You can sign up for a free demo here.

AI in Qualitative Analysis
AI offers a game-changing boost to qualitative analysis, streamlining processes with quicker data processing and surfacing hidden patterns that might not be perceptible to humans. It dives deep into the contextual fabric of qualitative data, helping researchers grasp nuances that enrich understanding. Emotional insights add another layer of detail to the overall insights, helping researchers enhance the quality of insights and hence the decisions driven by them.
By spotting complex cases and outliers, AI adds depth to the analysis. Beyond its analytical prowess, AI fosters inclusivity in academia by levelling the playing field, granting researchers from all backgrounds access to advanced tools and resources, empowering them to pursue meaningful and independent research endeavours.
One such AI-based tool for qualitative research is Lightbulb’s Insights Pro Quantitative that uses facial coding, voice transcription, and image processing to analyse live and recorded interview sessions. This helps reduce manual effort from the entire process and offers a speedy turnaround time for instantaneous results. You can sign up for the free demo here.
Advantages and Challenges of Using AI in Market Research
Greater Efficiency
Richer Insights
Automation of Redundant Processes
Custom Surveys
Early Trend Identification
Enhanced Scalability and Accessibility
Over Automation
Lack of Synergy Between Quantitative and Qualitative Teams
Fighting Privacy Issues
Lack of Dedicated In-House Resources
Some Real-World Examples of AI being Used in Market Research
Amazon
Popular AI-Powered Market Research Tools
Pecan AI

Speak
Appen
About Insights Pro
Request a Live Demo!
See how Facial Coding can
help your business
Book your slot now!
Other technologies similar to facial coding
Latest from our Resources
AI-Driven Innovation: Redefining Best Practices in UI/UX Testing
Introduction User interface and user experience testing (UI/UX testing) are two principal factors that behave as momentum for software development process providing digital solutions with top notch user friendliness and high level of users satisfaction. As a
Read MoreAI-Assisted UI/UX Testing: A Game-Changer in Product Development
Introduction: As users adopt digital products, delivering a flawless and remarkable user experience becomes one of the most critical
Read nowFacial Coding AI: Everything you need to know
This questions perhaps has lingered in our minds several times; why can we not easily hide our emotions as we do with our physical
Read nowFrequently Asked Questions
Facial expressions coding involves capturing and interpreting facial muscle movements known as action units (AUs). Each AU corresponds to specific emotions, providing a systematic way to decode facial expressions.
The Facial Action Coding Scheme (FACS) is a comprehensive system developed for precisely describing facial expressions. It assigns numerical codes to different facial movements, aiding in understanding emotional states across diverse contexts.
Facial expression analysis is a methodical examination of facial behaviors to decipher underlying emotions or reactions. It encompasses studying the intensity, duration, and sequence of facial movements to gain insights into emotional responses.
Emotion detection technology utilizes various techniques, including facial emotion recognition through computer vision algorithms, analyzing physiological signals like heart rate variability, voice modulation analysis, and sentiment analysis of text data, enabling a multidimensional.
Facial expression analysis involves scrutinizing facial movements to discern emotional cues. By analyzing the dynamics of facial expressions, researchers and practitioners can glean valuable information about individuals’ emotional states and responses to stimuli.
Although there are six primary facial expressions recognized universally—happiness, sadness, anger, surprise, fear, and disgust—there’s a spectrum of nuanced expressions reflecting complex emotional experiences. While these basic expressions serve as foundational categories, human emotions are multifaceted and diverse, leading to a myriad of facial expressions beyond the fundamental six.